Structural and numerical chromosomal abnormalities affect either the autosomes or gonosomes and are a common cause of spontaneous abortion. The most frequently observed autosomal abnormalities are trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome), trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), and trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). Individuals with these conditions have an extra copy of the chromosome to which their names refer. The risk of autosomal abnormalities increases with maternal age. Characteristic features include facial and skeletal malformations, which are usually recognizable at birth. The conditions are also associated with congenital heart defects and malformations of other internal organs. Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome are gonosomal abnormalities in which individuals have a missing X chromosome or an additional X chromosome, respectively. These conditions are primarily characterized by impaired development of secondary sexual characteristics and infertility secondary to gonadal dysgenesis. The diagnosis for all chromosomal abnormalities is confirmed with karyotyping.
Definitions
-
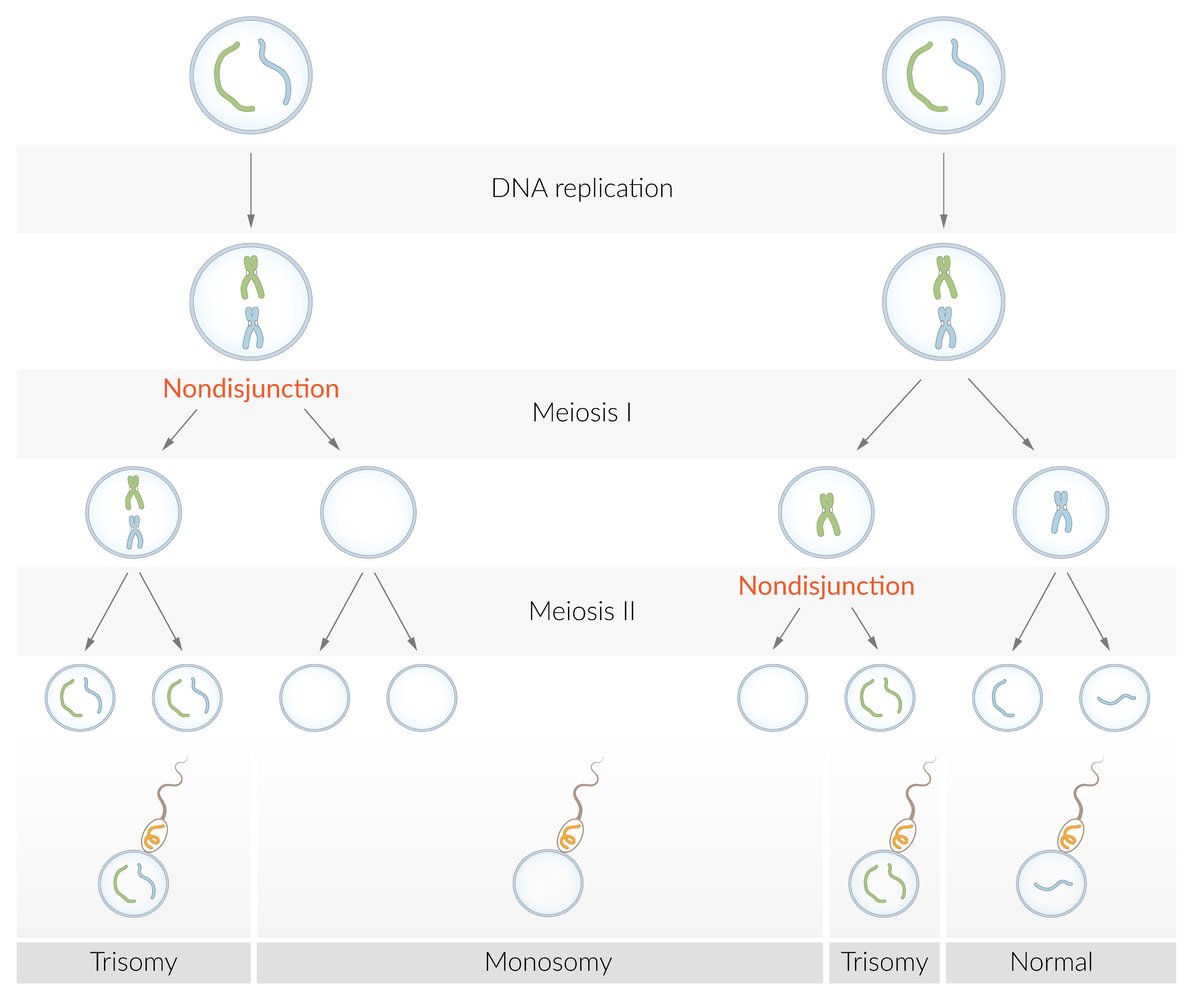
Chromosomal abnormality: deviation from the normal chromosome constellation
- Numericalchromosomal abnormality; (e.g., aneuploidy, polyploidy)
- Structuralchromosomal abnormality; (e.g., deletion, translocation)
- Triploidy: : presence of three sets of chromosomes
- Trisomy: : presence of triplicate instead of a duplicate number of a particular chromosome or part of a chromosome
Epidemiology
-
Chromosomal abnormalities are the most common cause of spontaneous abortion (accounting for 60% of cases).
- Approx. 50% of anomalies are trisomies.
- Approx. 20% of anomalies are triploidies.
Viable numerical chromosomal abnormalities
Autosomal chromosomal abnormalities
| Overview of autosomal chromosomal abnormalities | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) | Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) | Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) | |
| Karyotype |
|
|
|
| Pathogenesis |
|
|
|
| Clinical features |
|
|
|
| Associated conditions |
|
|
|
| Neurocognitive deficiency |
|
|
|
| Life expectancy |
|
|
|

Gonosomal chromosomal abnormalities
- Klinefelter syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- 47,XYY syndrome
- 47,XXX syndrome
-
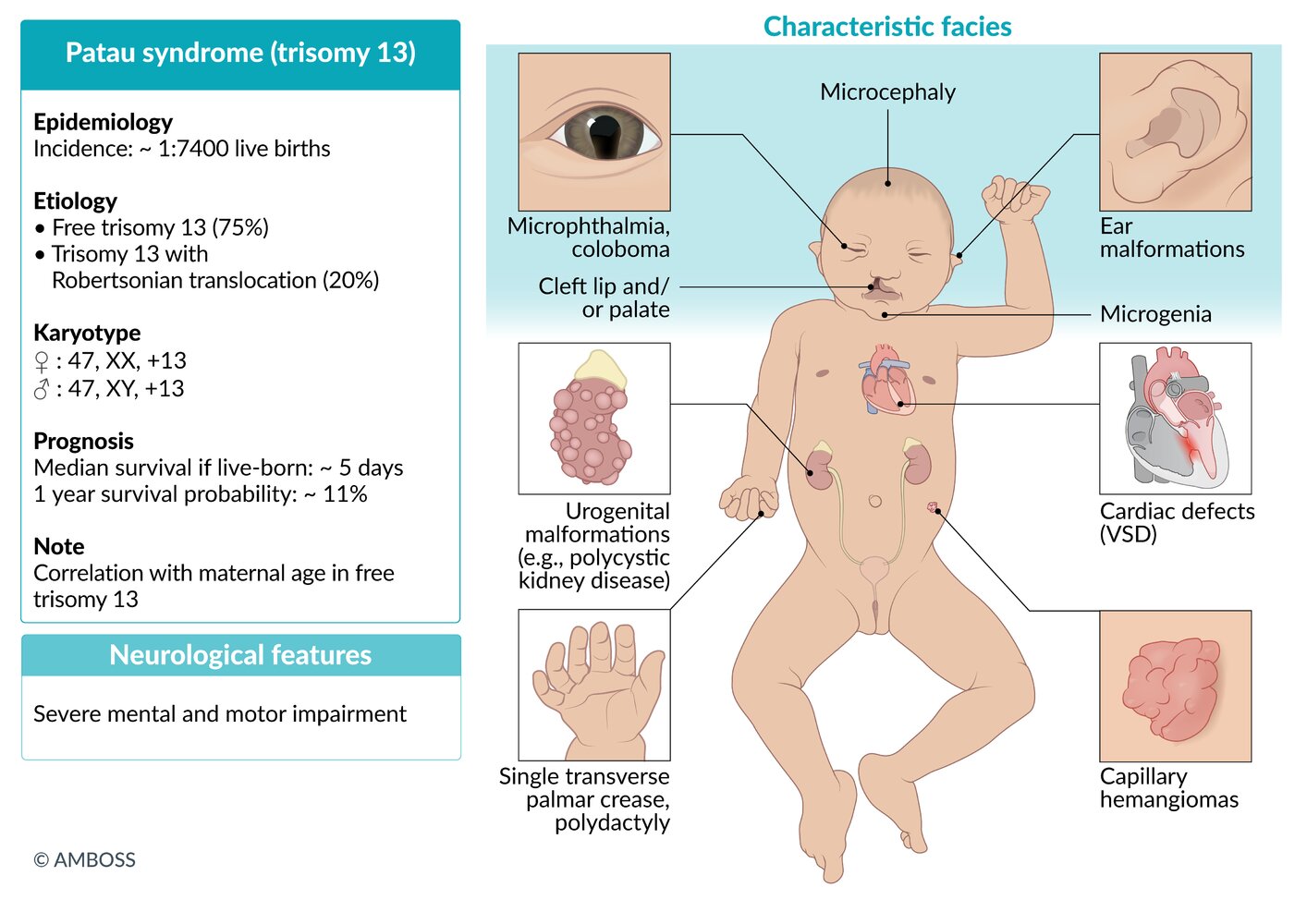
Karyotype
- ♀: 47,XX,+13
- ♂: 47,XY,+13
- Incidence: ∼ 1:7,400live births [1]
-
Pathogenesis
- Meiotic nondisjunction
- Abnormal fusion of prechordal mesoderm → midline defects
-
Clinical features
- Microcephaly, holoprosencephaly
- Characteristic facial anomalies
- Cleft lip and palate
- Low-set, malformed ears
- Bulbous nose
- Small chin
- Microphthalmia; (small orbits, which may be unilateral or bilateral), possibly coloboma, ocular hypotelorism
- Polydactyly (primarily hexadactyly), flexed fingers
- Congenital heart defects (particularly ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus)
- Rocker-bottom feet
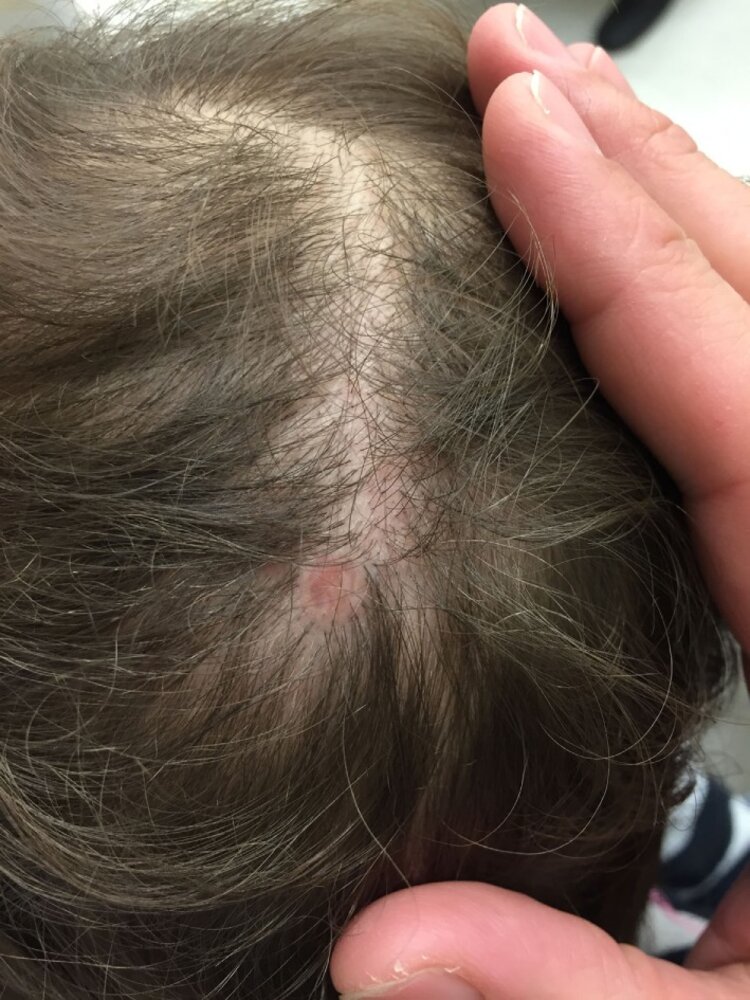
- Aplasia cutis congenita; : congenital absence of skin; most commonly scalp lesions with a punched-out appearance that may extend to the bone or the dura
- Omphalocele
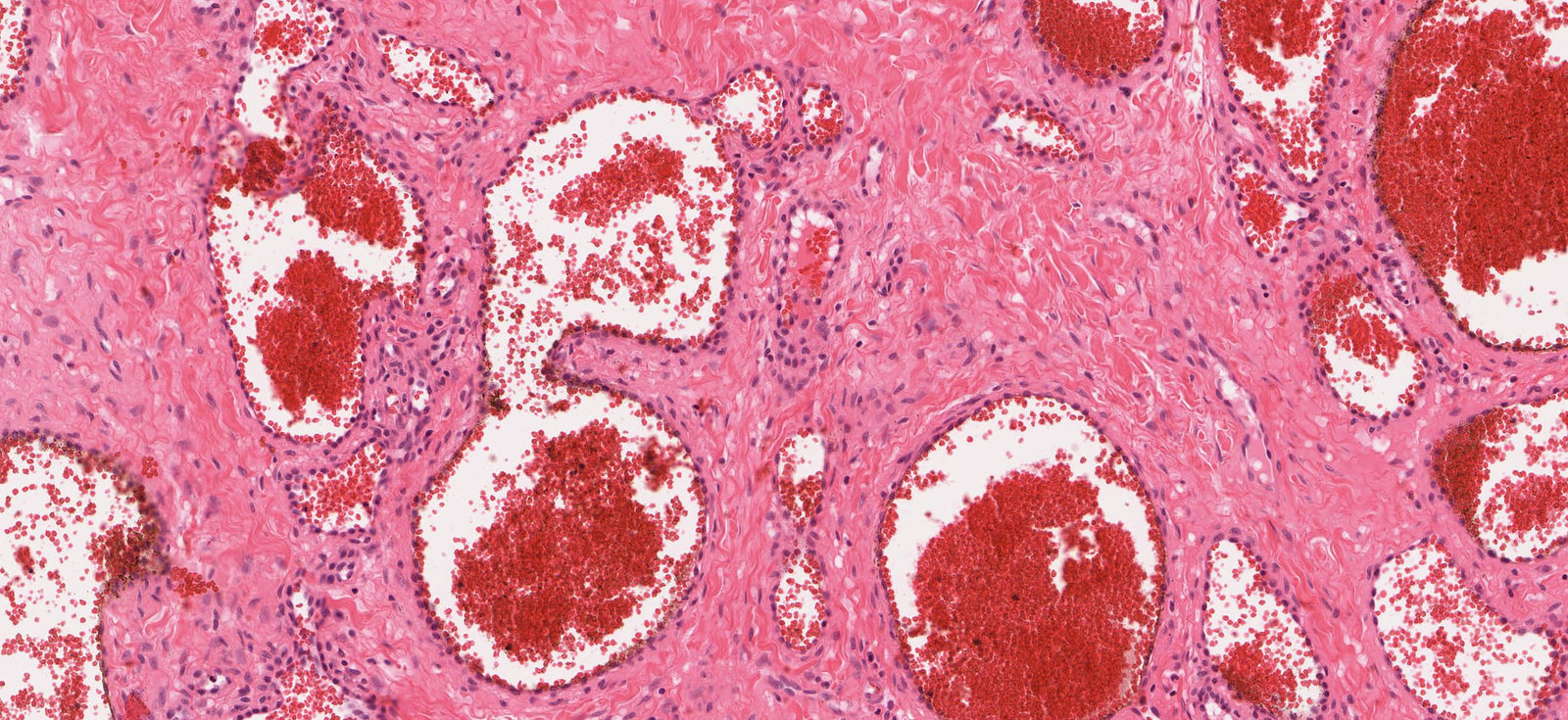
- Visceral and genital anomalies, especially of the kidneys and ureters (e.g., polycystic kidney disease)
- Capillary hemangioma
-
Diagnostics
- Usually detected during first trimester screening with combined ultrasound and maternal serum testing (↓ PAPP-A, ↑ nuchal translucency)
- See “Prenatal diagnostics.”
- Prognosis: Only approx. 11% of patients survive past 12 months of age. [2]
The age of Puberty onset is 13: Patau syndrome is caused by trisomy 13.
7 Ps of Patau syndrome: holoProsencephaly, cleft liP and Palate, Polydactyly, Pump disease (congenital heart disease), Polycystic kidney disease, cutis aPlasia.


-
Karyotype
- ♀: 47,XX,+18
- ♂: 47,XY,+18
-
Incidence
- ∼ 1:3,300live births [1]
- After trisomy 21, trisomy 18 is the most common autosomal trisomy in which fetuses can survive to birth.
- Pathogenesis: meiotic nondisjunction
- Gender: ♀ > ♂
-
Clinical features
- Characteristic facial anomalies
- Low-set ears (malformed auricle)
- Micrognathia (congenital mandibular hypoplasia)
- Prominent occiput
- Microcephaly
- Broad nose
- Cleft lip and palate, high palate
- Clenched fists with flexioncontractures and overlapping fingers
- Rocker-bottom feet: convex deformity of the plantar side of the foot, with a vertical talus, and prominent calcaneus
- Congenital heart defects (particularly VSD, ASD, tetralogy of Fallot)
- Malformations of internal organs: diaphragmatic hernia, ureter, and kidneys (horseshoe kidneys)
- Myelomeningocele
- Omphalocele
- Severe intellectual disability
- Characteristic facial anomalies
-
Diagnosis
- Quadruple test; in the second trimester shows ↓ free estriol, ↓ AFP, ↓ β-HCG, and normal/↓ inhibin A
- See “Prenatal diagnostics.”
- Prognosis: Only approx. 13% of patients survive past 12 months of age. [2]

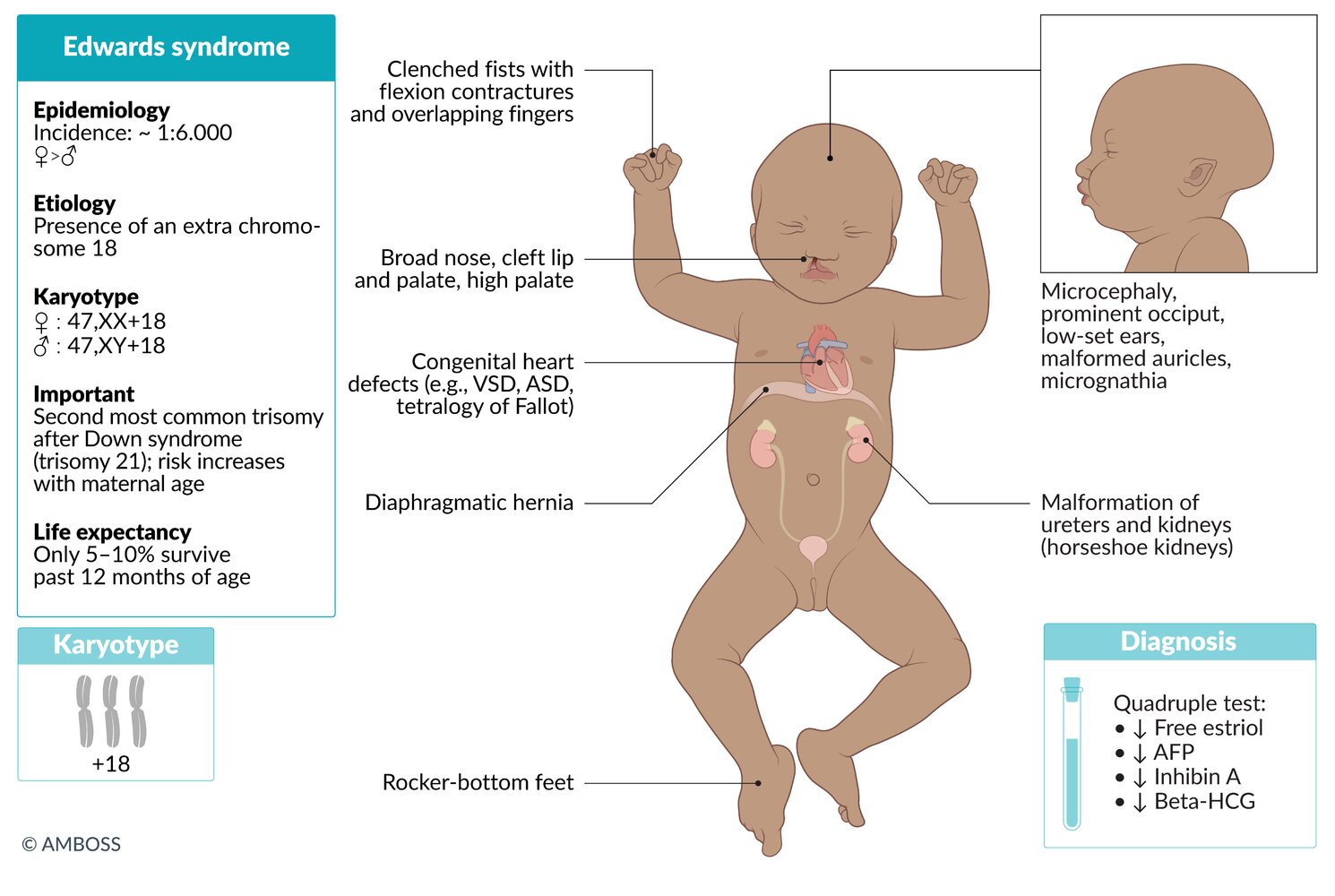

PRINCE Edward turned 18: Prominent occiput, Rocker-bottom feet, Intellectual disability, Nondisjunction (in meiosis), Clenched fists, low-setEars, and chromosome 18.
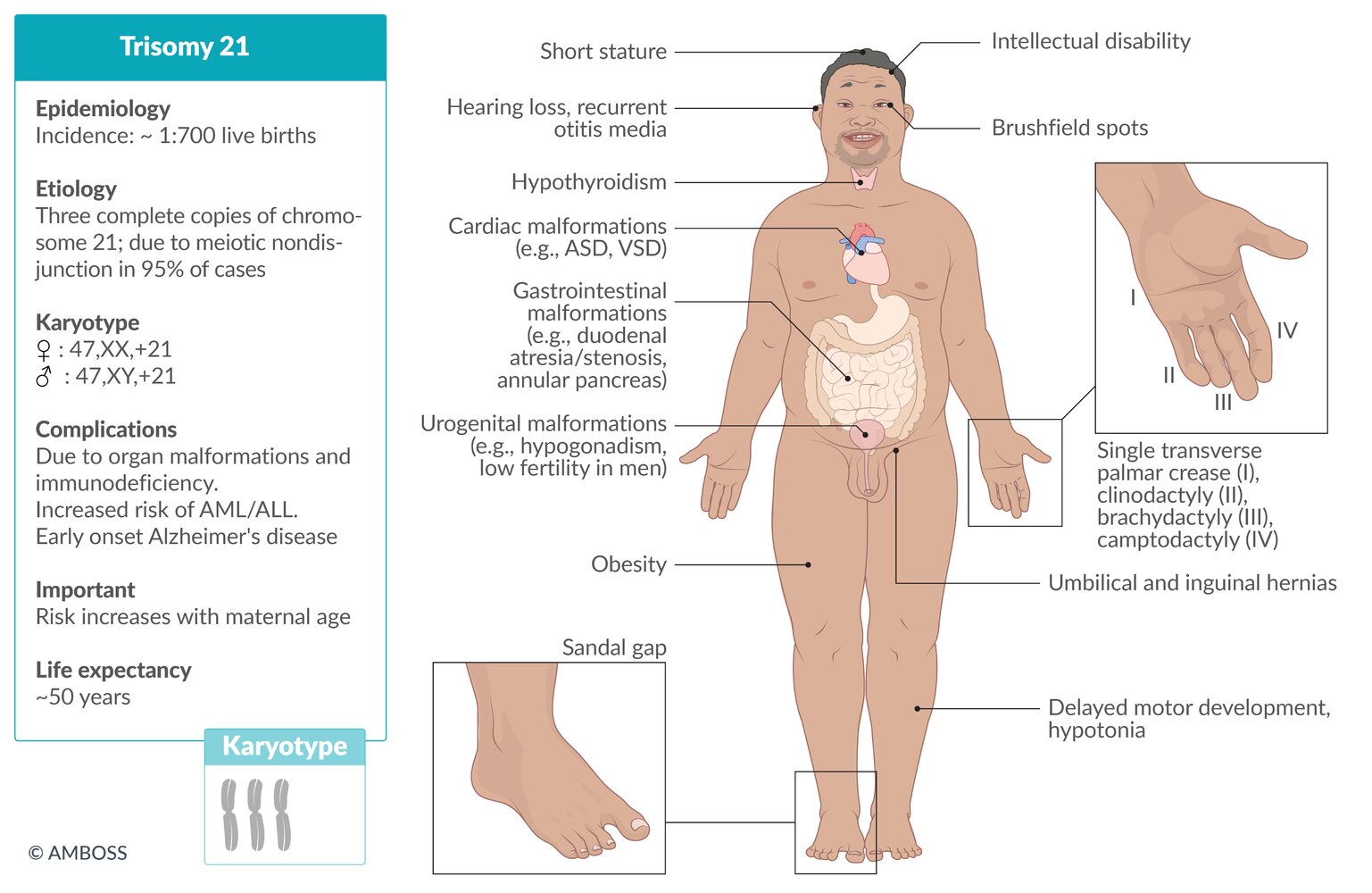
See article on “Down syndrome.”
-
Karyotype
- ♂: 47,XYY
- ♀: 47,XXX
-
Incidence [3][4]
- 47,XYY syndrome: ∼ 1/1,000 male newborns
- 47,XXX syndrome: ∼ 1/1,000 female newborns
-
Clinical features
-
47,XYY syndrome [5]
- Tall stature
- Mild delays in motor and language development
- Possible fertility problems (decreased sperm count)
-
47,XXX syndrome [6]
- Tall stature
- Delayed motor and language development
- Learning disabilities
- Menstrual abnormalities, occasionally fertility problems
-
47,XYY syndrome [5]
-
Diagnosis [7]
- The majority of women with triple X and men with double Y are never diagnosed.
- Chromosome analysis
-
Treatment
- Only symptomatic treatment is possible.
- Speech therapy
- Physical, occupational, and educational therapy
- Reproductive specialist in individuals with fertility problems